Chapter 5: clause type III
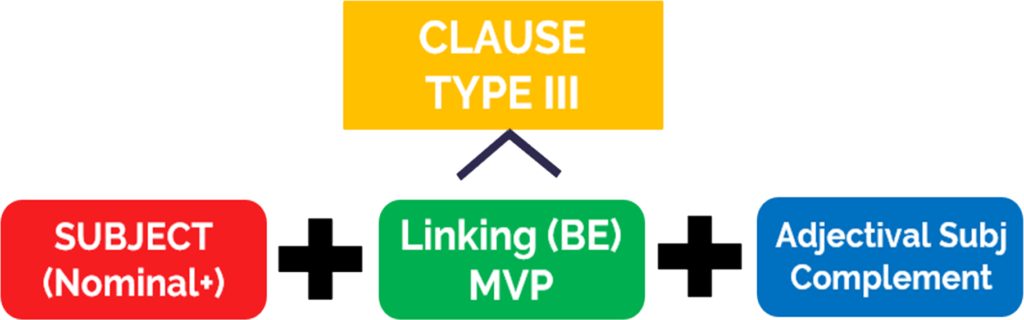
In this clause type, the function slot that follows the linking verb is reserved for a subject complement (an adjectival function slot), which modifies or describes the subject, but also completes the verb. In the case of a type III clause, the subject complement is always adjectival. Consider the following:
-
Adjective: The soldiers were diligent in their duty.
-
Adjectival phrase: They are in good spirits.
-
Adjectival clause: They look as if they could take on the world.
Sentences (1) through (3) all exemplify Type III clauses. Sentence (1) is prototypical, with a clear adjective; however, sentence (3) is a bit more difficult to break down. We have the linking verb look, but a clause is in the complement slot. In this case, we can determine if the clause is acting adjectivally by attempting to replace the entire clause with a single adjective, such as prepared. We can do the same for sentence (2) by replacing the prepositional phrase with a happy.
In analyzing for Type III clauses, we look for the BE/linking verb, followed by an adjectival (word, phrase, or clause) in the function slot.
AND ONE FINAL NOTE: you will be expected to “type” all clauses in
a particular sentence. Sentences (1) and (2) have only one clause, but
sentence (3) would require that you “type” both clauses:
-
They look as if they could take on the world. – Type III (linking verb + adjectival clause)
-
as if they could take on the world – Type V (transitive verb + nominal direct object)

